Parkinson S Disease Brain Areas Affected

Areas most often affected include.
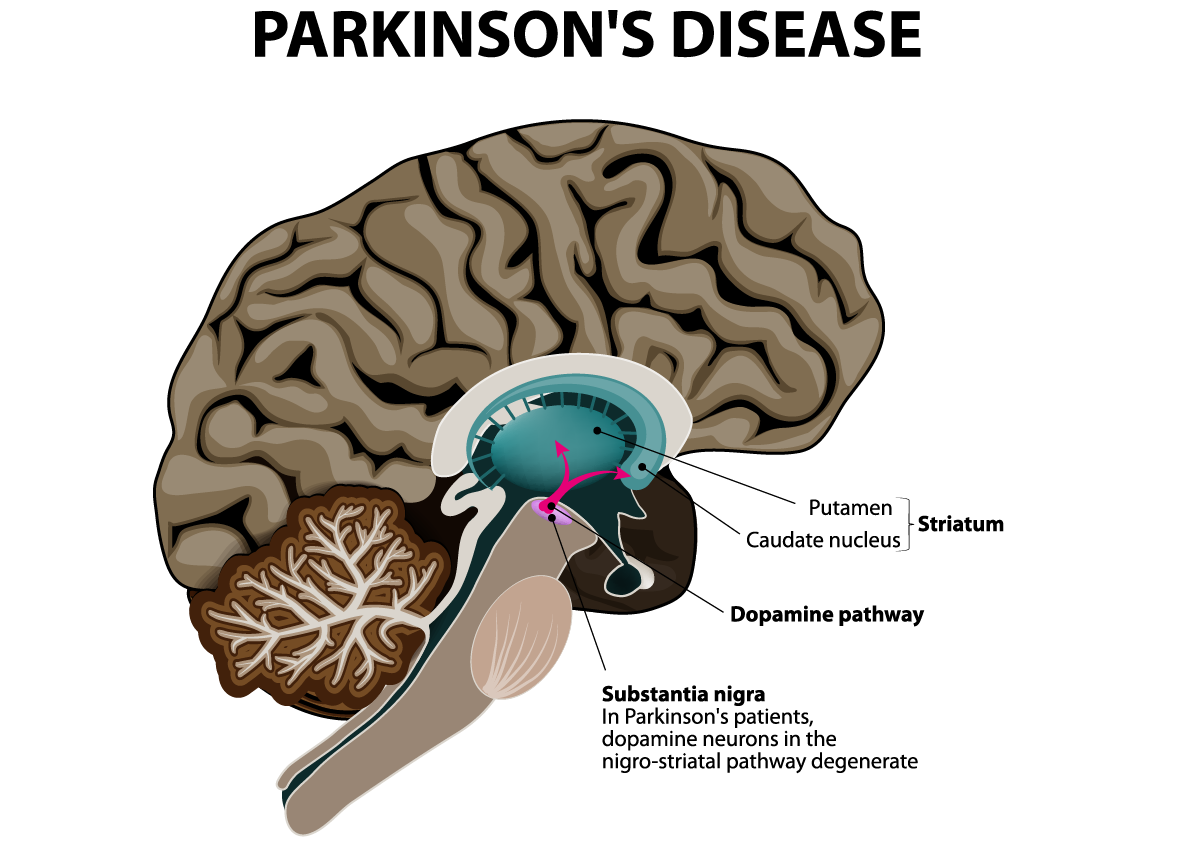
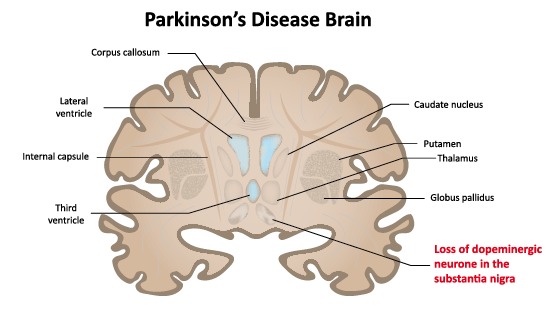
Parkinson s disease brain areas affected. Parkinson s disease pd is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine producing dopaminergic neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra. To understand parkinson s it is helpful to understand how neurons work and how pd affects the brain see anatomy of the brain. Parkinson s disease occurs when nerve cells or neurons in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and or die. Parkinson s disease occurs because of a deterioration of neurons in an area of the brain called the basal ganglia.
Symptoms generally develop slowly over years. When dopamine levels decrease it causes abnormal brain activity leading to symptoms of parkinson s disease. There are three areas of the brain that most affected. It is named after dr james parkinson who first described the condition in 1817.
Many of the symptoms are due to a loss of neurons that produce a chemical messenger in your brain called dopamine. Normally these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. In parkinson s disease certain nerve cells neurons in the brain gradually break down or die. Difficulty with complex tasks that require person with pd to maintain or shift their attention.
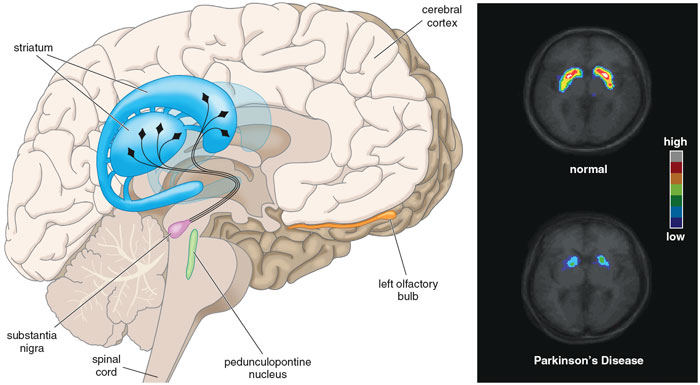
The cognitive changes that accompany parkinson s early on tend to be limited to one or two mental areas with severity varying from person to person. It is progressive and symptoms worsen over time. The subthalamic nucleus a nerve center near the substantia nigra. Hence the popular name jitters.
Parkinson s disease is a chronic long term neurological condition. Parkinson s typically strikes the age group 50 to 70 years. The globus pallidus another nerve center responsible for movement balance and walking. People with parkinson s disease experience a loss of nerve cells in the part of their brains responsible for controlling voluntary movements.
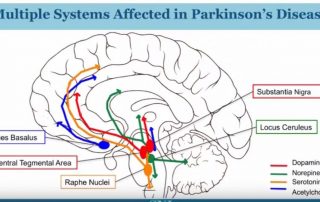
Parkinson s disease affected brain regions and associated neurological dysfunctions. Nerve cells or neurons are responsible for sending and receiving nerve impulses or messages between the body and the brain. The more marked caudate reduction suggests that raphe neurons innervating this area are more susceptible to damage than those innervating putamen and that any functional impairment caused by striatal serotonin loss might primarily involve. When the neurons die or become impaired they produce less dopamine which causes the movement problems of parkinson s.