Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology

As per statistics type 2 diabetes is the most commonly occurring type in comparison to the other two forms of diabetes mellitus.
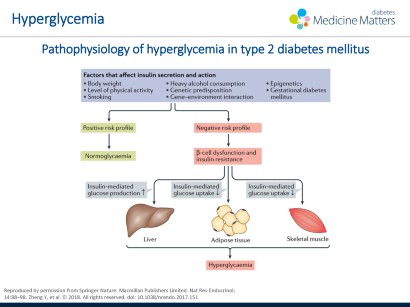
Type 2 diabetes mellitus pathophysiology. Pathology of type 2 diabetes in type 2 diabetes the body either produces inadequate amounts of insulin to meet the demands of the body or insulin resistance has developed. With type 2 diabetes your body either resists the effects of insulin a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells or doesn t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by peripheral insulin resistance impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production and declining β cell function eventually leading toβ cell failure. Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by hyperglycemia and resulting from the combination of resistance to insulin action inadequate insulin secretion and.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar glucose an important source of fuel for your body. Diabetes mellitus type 2. In addition to type 2 diabetes the metabolic syndrome is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease the main complication of type 2 diabetes see chapter 13 6 1. Regarding the definition of diabetes mellitus it is often described as a fasting blood glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter mg dl or more.
The causes of type 2 diabetes are multi factorial and include both genetic and environmental elements that affect beta cell function and tissue muscle liver adipose tissue and pancreas insulin sensitivity. The development of type 2 diabetes overt hyperglycaemia also requires the presence of a relative defect in insulin secretion.