Mri Findings In Parkinson S Disease Radiographics

Mri signs of parkinson s disease mimics.
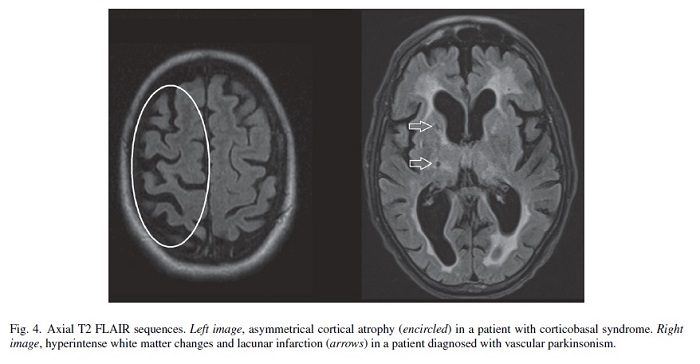
Mri findings in parkinson s disease radiographics. By dr andrew dixon. Although these cannot be definitively diagnosed or differentiated from parkinson s disease pd with mri there are radiologic hallmarks that can be useful when combined with the clinical examination and other diagnostic tests. Most prominent in the distal upper limbs. The classic cardinal motor features of parkinson disease which are often asymmetric include.
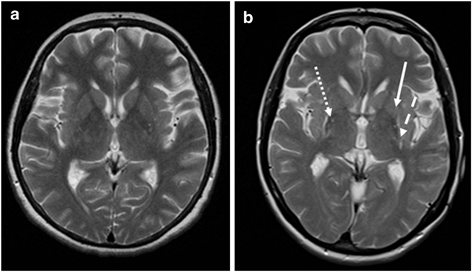
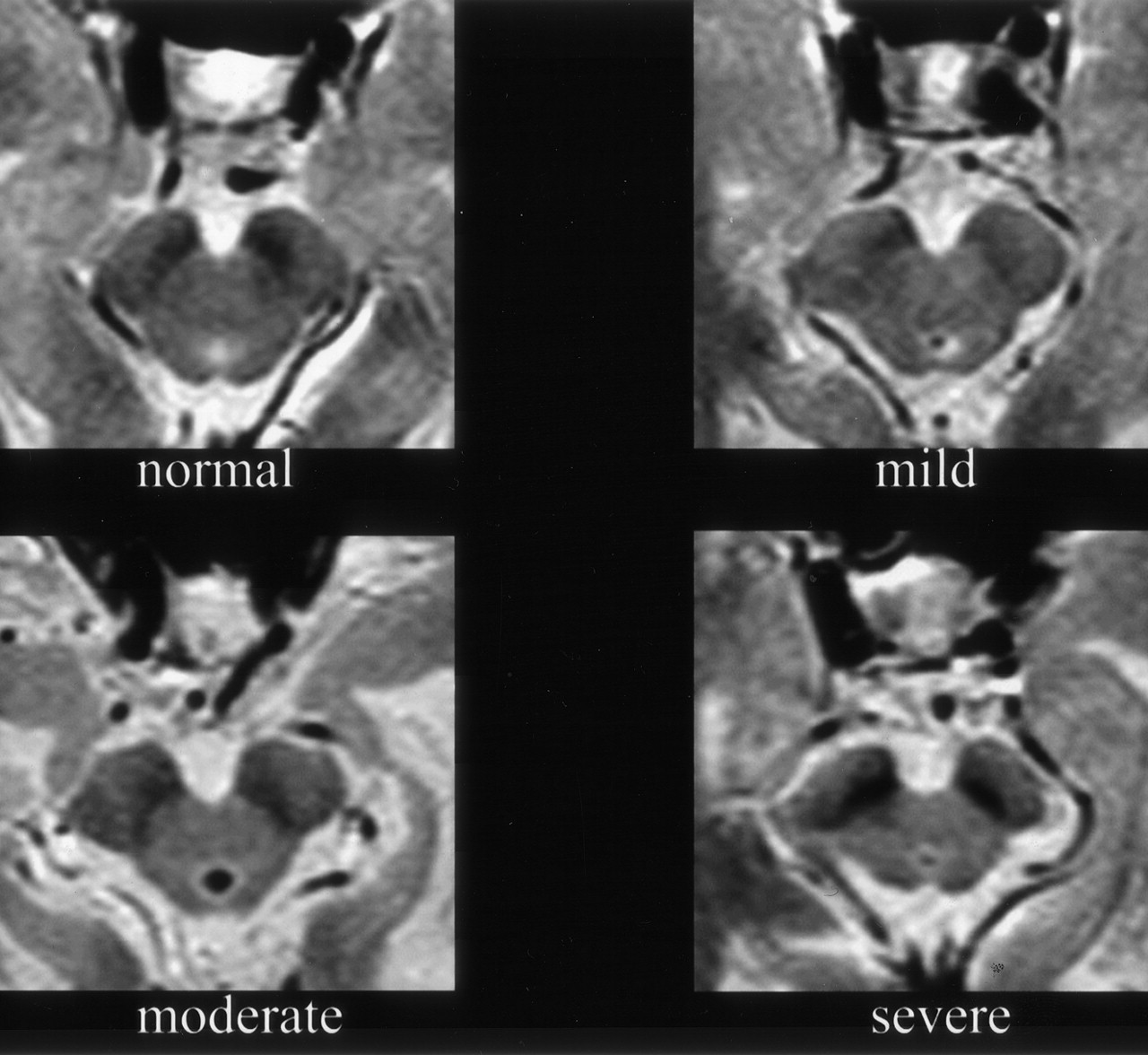
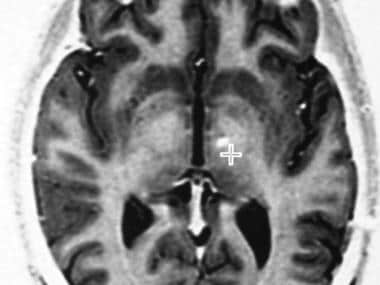
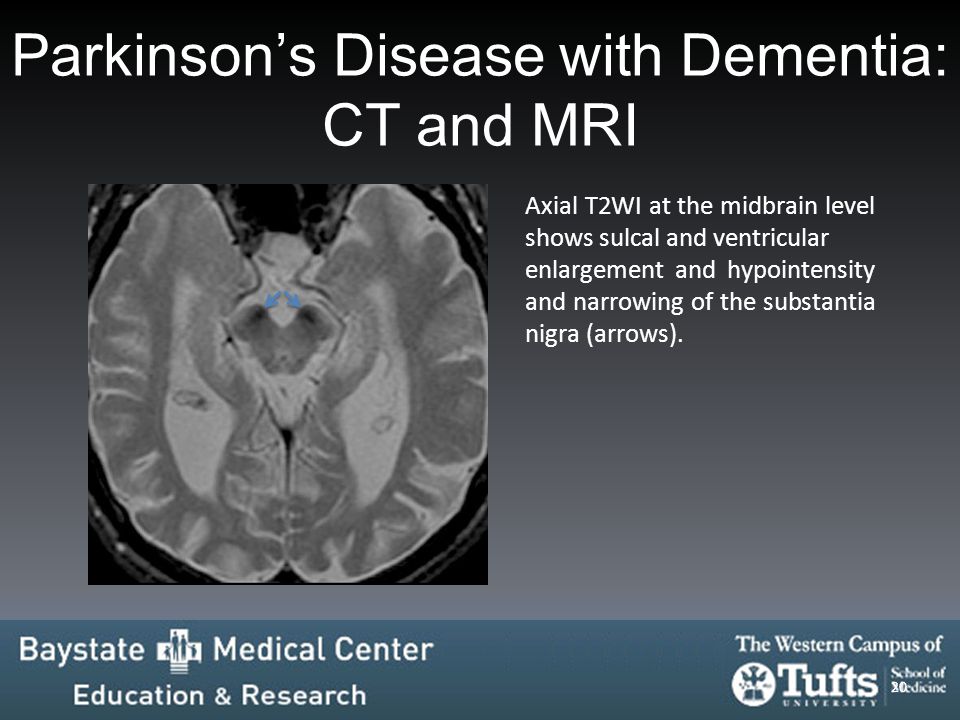
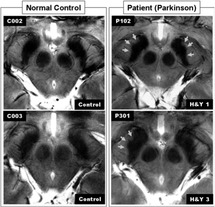
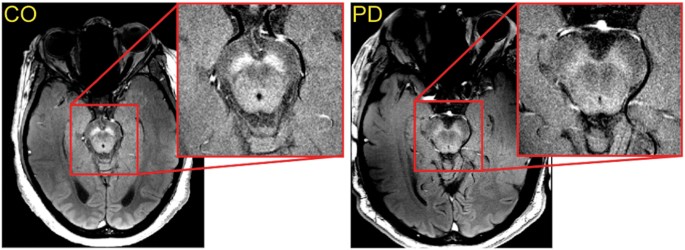
In advanced disease abnormalities of the substantia nigra including volume loss decreased t2 signal reflecting iron deposition and blurring of the margins can be seen 26 28. A reduction in the area of the substantia nigra sn has been shown in patients with parkinson disease. The substantia nigra is anteroinferolateral to the red nucleus and it is important to precisely locate its true anatomic location to accurately measure sn area. Although no single imaging test is diagnostic a combination of tests may help narrow the differential diagnosis.
Magnetic resonance parkinsonism index maung maung soe and dr marcin czarniecki et al. Fdg pet uptake can demonstrate patterns of neuronal dysfunction that are specific to a particular parkinsonian syndrome. A recent research publication in plos one has described a new 3t mri sign of parkinson disease known as the absent swallow tail sign. Radiographic features mri is the modality of choice for imaging patients with suspected multiple system atrophy msa.
In 2016 experts developed new criteria for. Toxic and metabolic brain disorders manifest secondary to derangements of a well balanced environment encompassing metabolic substrates neurotransmitters electrolytes physiologic ph levels and blood flow either by endogenous malfunctions or exogenous toxic effects. This article addresses some of the most challenging diagnostic issues in neuroimaging. Our purpose was to determine the exact location of the substantia nigra by correlating imaging and.
Share on pinterest an mri or ct scan can help to distinguish parkinson s from other conditions that may have similar symptoms such as a stroke. The discovery which has the potential to revolutionise the diagnosis of this important disease uses axial high resolution susceptibility weighted imaging swi to assess the structure of the substantia nigra within the midbrain. However the primary use of mr imaging is to exclude specific structural abnormalities that could potentially mimic parkinson disease eg normal pressure. Several neurodegenerative diseases can cause parkinsonian motor symptoms.
Unlike parkinson disease and lewy body dementia two other synucleinopathies these intracellular deposits are found not only in neurons but also in oligodendroglia 2. Magnetic resonance parkinsonism index mrpi can be used in mri studies to predict the presence of progressive supranuclear palsy psp in patients with clinically unclassifiable parkinsonism. Classically 5 hz pill rolling resting tremor.