Leukemia Bruises Children

Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and teens accounting for almost 1 out of 3 cancers.
Leukemia bruises children. I noticed some unexplained bruises on my right hand and lower limbs. That can set the stage for bruising. In addition to easy bruising bleeding and a low platelet count children with leukemia will usually have other signs and symptoms such as a low red cell count fever and weight loss for example. If a child bruises easily experiences severe nosebleeds or bleeds from the gums this can point to leukemia.
If aml spreads to the skin it can cause small dark spots that look like common rashes. When platelets become low patients often bleed into. A child with leukemia may complain of a stomachache. Most childhood leukemias are acute lymphocytic leukemia all.
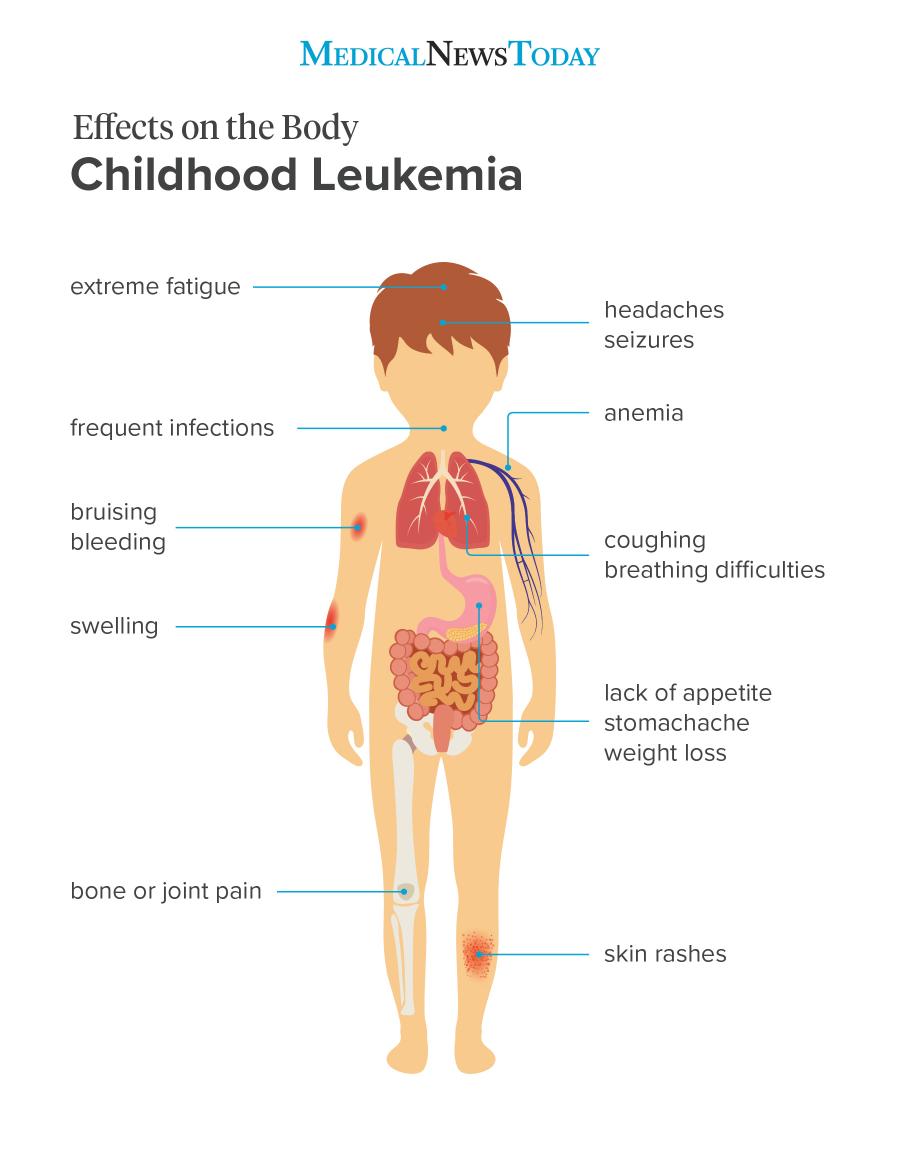
Childhood leukemia the most common type of cancer in children and teens is a cancer of the white blood cells abnormal white blood cells form in the bone marrow. This is because leukemia cells can. Stomachache and poor appetite. Symptoms of childhood leukemia bruising and bleeding.
Leukemia can cause tiny blood vessels called capillaries to burst underneath the skin. Feeling unusually tired or weak fever or chills unexplained weight loss nighttime sweating frequent nosebleeds occasional rashes and bruises on the skin. They occur in unusual places in cases of leukaemia quite often bruises will appear in places that you wouldn t normally expect especially. Leukemia can disrupt the body s production of platelets which normally form blood clots to stop bleeding.
For children bruises may start to appear on the face buttocks ears chest and head. In children with acute myeloid leukemia aml leukemia cells may spread to the gums causing swelling pain and bleeding. Chronic leukemias are rare in children. When leukemia progresses to a certain point the multiplication of abnormal blood cells disrupts the.
They quickly travel through the. Rashes or gum problems. The back legs and hands. A child with this type of cancer will have a lack of platelets that help to prevent.

/girl-with-a-bruised-knee-585107377-594468a05f9b58d58a681b3b.jpg)